As we stand on the threshold of a new era, the world of industrial design is undergoing a seismic shift, reflecting the convergence of technology, sustainability, and human-centric innovation. From smart materials to eco-efficient production methods, the future of industrial design is not merely about aesthetics or functionality; it is an intricate dance of creativity and practicality that seeks to redefine our everyday experiences. In this exploration, we delve into the top trends that are set to shape tomorrow’s innovations, illuminating the pathways where design meets the pressing challenges of our time. Join us as we navigate this dynamic landscape, discovering how visionary ideas are transforming industries and preparing us for a future where design does more than serve—it transcends, inspires, and connects.
Exploring the Role of Sustainability in Modern Industrial Design Innovations

As the conversation around sustainability gains momentum, modern industrial design is increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly practices that reflect a commitment to a greener future. Innovative designers are now focusing on utilizing recyclable materials, adopting a circular economy approach, and integrating biomimicry principles to create products that are not only functional but also environmentally responsible. This shift has resulted in designs that minimize waste and maximize efficiency, ultimately reshaping the way industries think about product lifecycles.
The role of sustainability in industrial design has also paved the way for groundbreaking technologies and methodologies. As an example, 3D printing allows for precise material usage with reduced waste, while smart materials can adapt to their habitat, optimizing energy consumption. Here are some emerging sustainable trends reshaping this field:
- Modular Design: Products designed for easy disassembly and reuse.
- Upcycling: Transforming waste materials into new, useful products.
- Eco-friendly Manufacturing: Processes that reduce carbon footprint and pollution.
| Technology | Impact on Sustainability |
|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Reduces waste by allowing precise control over materials used. |
| Biomimicry | Inspires designs that work in harmony with nature. |
| Smart materials | Enhances durability and energy efficiency in products. |
The Intersection of Technology and Creativity in Future Product Development

The fusion of technology and creativity is redefining product development by enabling designers to push the boundaries of innovation. As advanced tools like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) become integral to the design process, thay allow for unprecedented levels of customization and efficiency. Designers now leverage data-driven insights to understand user preferences and predict future trends, thus fostering a more user-centric approach. The incorporation of sophisticated software not only streamlines the workflow but also enhances collaboration, allowing cross-disciplinary teams to merge their unique perspectives and create truly groundbreaking products.
Emphasizing sustainability and social impact is shaping the creative process in industrial design as well. Companies are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly materials and methods, fostering a new wave of innovation that balances profit with responsibility. Key strategies include:
- Utilizing biodegradable materials
- implementing circular design principles
- Adopting energy-efficient manufacturing techniques
As these practices become standard, they not only offer a competitive edge but also resonate with a consumer base that is increasingly conscientious about their choices. The future of product development lies in the harmonious blend of technological advancement and creative exploration, setting the stage for innovations that are not only functional but also ethical and sustainable.
Minimalist Aesthetics: Reflecting Simplicity in Industrial Design Trends

Minimalist aesthetics have emerged as a significant influence in industrial design, embodying the principle of “less is more.” This design beliefs emphasizes clean lines, open spaces, and functionality, creating products that not only fulfill their purpose but also resonate visually. By stripping away unnecessary embellishments, industrial designers focus on the core elements of their creations, leading to an organized and cohesive appearance. Key characteristics of minimalist design include:
- Neutral Color Palettes: Soft, muted tones that enhance clarity and simplicity.
- simple Shapes: Geometric forms that deliver functionality without excess.
- Natural Materials: Use of wood, metal, and stone to convey authenticity and durability.
- Thoughtful Space Utilization: Designs that promote efficiency and ease of use.
As industries move toward sustainability, the minimalist approach aligns perfectly with eco-conscious practices. By reducing materials and focusing on essential components,designers not only craft aesthetically pleasing products but also contribute to waste reduction and energy efficiency. This convergence of form and function results in innovations that are as environmentally friendly as they are visually striking. Consider the following trends redefining minimalist design:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Modular Designs | Interchangeable parts that adapt to user needs. |
| Smart Technology Integration | Seamless incorporation of technology into simple designs. |
| Upcycled Materials | Using repurposed materials to create new products. |
Biophilic Design Principles: Connecting Nature with Urban Environments

As urban environments expand, incorporating elements of nature within our design principles is becoming essential for promoting well-being and sustainability. By integrating natural materials, colors, and patterns, designers can create spaces that evoke the tranquility found in nature. Some effective strategies include:
- natural Light: Maximizing sunlight through large windows and open spaces enhances mood and reduces reliance on artificial lighting.
- Green Spaces: Integrating plants and gardens not only beautifies a space but also improves air quality and promotes biodiversity.
- Water Features: Incorporating elements like fountains or water walls can provide soothing sounds and visual interest that mimic natural settings.
Moreover, the connection to nature in design extends beyond mere aesthetics; it fosters a sense of community and improves the overall quality of life for urban dwellers. This principle can manifest in various ways, such as:
| Design Element | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Biophilic Geometry | Encourages a sense of calm and enhances cognitive function. |
| Materials | Natural materials can reduce stress and create a comfortable atmosphere. |
| Local Flora | Supports local ecosystems and fosters environmental awareness. |
Smart Materials: Engineering Tomorrow’s Solutions for Modern Problems

Smart materials are paving the way for innovations that seamlessly integrate with modern life, addressing challenges in various industries. These materials are designed to respond dynamically to environmental changes, utilizing their unique properties to enhance functionality and efficiency. Examples of smart materials include:
- Shape-memory alloys: regain their original form after deformation, ideal for applications in robotics and aerospace.
- Self-healing polymers: repair themselves when damaged,greatly improving the longevity of products.
- Phase change materials: regulate temperature by absorbing or releasing heat, perfect for energy-efficient building designs.
As industries embrace these advanced solutions, the potential impact of smart materials on sustainability and resource management becomes apparent. For instance, their ability to minimize waste and enhance product lifespan contributes to a circular economy model. Innovations in smart textiles are also revolutionizing personal wearables, blending fashion with health monitoring. A comparison of customary vs. smart material applications illustrates this shift:
BEST-SELLING PRODUCTS IN THIS CATEGORY
| traditional Materials | Smart Materials |
|---|---|
| Static performance | Dynamically responsive |
| Limited lifespan | Self-repair capabilities |
| Higher energy consumption | Energy-efficient solutions |
User-Centric Design: Focusing on Experience to Drive Future Products

As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of industrial design, the core focus on user interaction and satisfaction is reshaping the way products are conceived. Adopting a user-centric approach ensures that the needs and preferences of consumers are at the forefront, leading to innovations that genuinely resonate with users.This design philosophy emphasizes the importance of understanding user behaviors and contexts, fostering deeper connections between people and products.Key aspects of this approach include:
- Empathy Mapping: Capturing the emotional and practical experiences of users to drive design decisions.
- Iterative prototyping: Using feedback loops to refine designs based on real-world user interactions.
- Inclusive Design: Ensuring products are accessible and usable by individuals of all abilities and backgrounds.
moreover, as industries increasingly adopt advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning, the potential to enhance user experiences grows exponentially. By harnessing data analytics, designers can forecast trends and personalize user interactions, creating products that not only fulfill functional requirements but also delight users in unexpected ways. This shift towards a more tailored experience is driving a new era of innovation, characterized by:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Devices | Integration of IoT technology to create intuitive, responsive products. |
| Sustainable materials | Adoption of eco-friendly materials that cater to environmentally conscious consumers. |
| Minimalistic Design | Focus on simplicity and functionality, enhancing user experience through uncluttered interfaces. |
The Rise of Modular Design: Transforming Spaces with Flexibility

The trend toward modular design is revolutionizing how we think about and utilize our spaces. This approach embraces the idea of flexibility and adaptability, allowing environments to evolve effortlessly as needs change. Modular systems offer advantages for both residential and commercial settings, as they can be reconfigured quickly without requiring extensive renovations. Key benefits include:
- Scalability: Adapt spaces to accommodate growth or downsizing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduce long-term expenses by minimizing demolition and construction costs.
- sustainability: Make use of sustainable materials that can be reused or recycled.
As living and working conditions continue to shift, the demand for versatile layouts will only increase. Innovations in technology play a significant role, allowing designers to create smart modular components that can integrate seamlessly with digital infrastructures. Consider the following attributes driving modular design:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Customization | User preferences influence layout options. |
| Interconnectivity | Modules that work together for enhanced functionality. |
| Rapid Deployment | Fast assembly reduces project timelines. |
Inclusive Design Approaches: Ensuring Accessibility as Standard Practice

The landscape of industrial design is rapidly evolving, with accessibility becoming a core principle rather than an afterthought. Companies are increasingly recognizing that inclusive design is essential in creating products that cater to a broader audience. This approach not only enhances usability for individuals with disabilities but also improves overall user experience for everyone. Designers are now collaborating with diverse groups, including those with different abilities, to ensure that their needs are met right from the ideation stage. By integrating accessibility features as standard practice, businesses are not only fostering innovation but also opening opportunities to untapped markets.
Key strategies for implementing this mindset involve incorporating adaptive technologies and utilizing design frameworks that prioritize user feedback. Crucial considerations include:
- Flexible Interfaces: Designing products that adapt to different inputs and environments.
- Universal Design Principles: Creating solutions that are intuitive and navigable by all users.
- Testing with Real Users: Engaging with a diverse audience during the testing phase to refine functionality and accessibility.
As we look towards the future, it’s evident that accessible design isn’t merely a trend but rather a foundational element of accomplished innovation. by embracing inclusivity, designers can create more resilient, user-friendly products that reflect the rich tapestry of human experience.
circular Economy: Redefining Waste and Resource Management in Design

the concept of a circular economy is gaining significant traction within industrial design as it challenges traditional notions of waste and resource management. By emphasizing regenerative practices, designers are now tasked with creating products that remain in use for as long as possible, ultimately reducing the need for raw material extraction. This approach not only conserves resources but also supplies innovative pathways through which products can be reused, repurposed, or recycled. Key strategies include:
- Design for Disassembly: Crafting products that can be easily taken apart promotes repair and refurbishment.
- Material efficiency: Utilizing sustainable and biodegradable materials reduces the environmental impact.
- Take-Back Programs: Encouraging consumers to return products at the end of their life cycle enables manufacturers to reclaim materials.
As designers embrace the principles of a circular economy, the importance of collaboration becomes paramount. Multidisciplinary teams are increasingly integrating perspectives from not only designers but also engineers, environmental scientists, and waste management experts. This collaborative effort facilitates a more holistic approach to product design, leading to innovative solutions that align with sustainability goals. The table below illustrates some noteworthy design innovations inspired by this transformative framework:
| Innovation | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradable Electronics | Devices that decompose after use, reducing e-waste. | Minimizes landfill contributions. |
| Modular Furniture | Furniture that can be easily adapted or rebuilt. | Extends product lifespan and usability. |
| Upcycled Materials | products crafted from discarded materials. | reduces resource extraction and waste. |
Ethical Production: Balancing Profit and Responsibility in Design Practices

In an era where consumers are increasingly aware of the impact their choices make, designers are finding innovative ways to align their practices with ethical standards.Emphasizing sustainability, eco-friendly materials, and responsible sourcing not only addresses environmental concerns but also meets the expectations of conscientious consumers.Designers are actively seeking methods to minimize waste through techniques like 3D printing and modular design, allowing for more efficient production processes that embody both creativity and ethical responsibility. some key strategies include:
- Material Innovation: using biodegradable and recycled materials in product design.
- Supply Chain Openness: Partnering with suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing processes that reduce energy consumption during production.
Additionally, the financial aspect of ethical production cannot be overlooked. While initially, sustainable practices may require a larger investment, the long-term benefits demonstrate a favorable return. Businesses that adopt responsible design practices frequently enough see an increase in brand loyalty as customers align with their values. A well-informed approach entails understanding the balance between profitability and social responsibility. As illustrated in the table below, companies that integrate ethical practices frequently report:
| Aspect | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Customer Retention | Higher loyalty and repeat purchases. |
| Brand Image | Improved perception in the marketplace. |
| Cost Savings | Reduction in waste and resource usage. |
the Influence of Cultural Trends on Future industrial Aesthetics

The cross-pollination of cultural trends and industrial design is becoming increasingly evident as we look towards the future. Today’s aesthetic choices in industrial design are heavily influenced by social movements, advancements in technology, and evolving consumer behaviors. As designers draw inspiration from the world around them, they are redefining the boundaries of functionality and aesthetics. This symbiotic relationship encourages the creation of products that not only meet practical needs but also resonate with the values and aspirations of contemporary society. For instance, the rise of sustainability has led to a preference for materials that echo environmental consciousness, compelling designers to innovate in how they source and utilize resources.
Moreover,technology continues to shape industrial aesthetics in profound ways. The integration of smart technology in everyday objects is altering how we perceive and interact with the products around us. Innovations such as AI-driven design tools and immersive virtual reality experiences are pushing the envelope, facilitating not just customizations, but also collaborative design processes that reflect a broader spectrum of cultural influences. As trends shift towards personalization and user-centric designs, the aesthetic of industrial products is becoming a canvas for expressing identity. This evolution emphasizes a cohesive blend between practicality and artistic expression, allowing designers to capture the essence of diverse cultural narratives and translate them into tangible, innovative solutions.
3D Printing Innovations: Revolutionizing Customization in Product Design
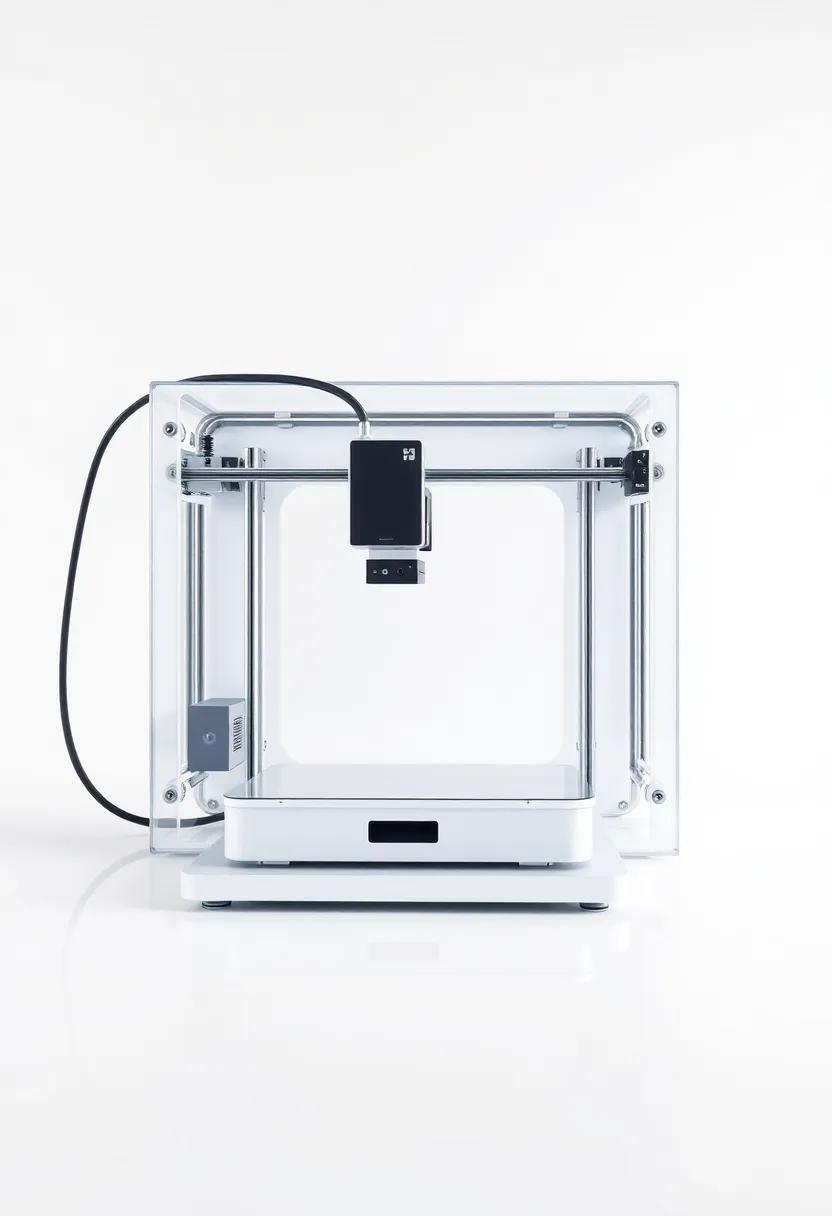
3D printing has emerged as a transformative force in the realm of product design, ushering in an era where customization reaches unprecedented heights. Gone are the days when mass production dictated uniformity; now designers can harness technology to create tailored solutions that meet individual needs.This innovation allows for the seamless integration of complex geometries and the use of diverse materials, resulting in products that are not only functional but also aesthetically unique. With advances in materials science, designers can experiment with everything from recycled plastics to bio-based composites, broadening the horizons of creativity and sustainability.
As industries embrace this cutting-edge technology, the benefits of on-demand production become increasingly apparent. companies can now reduce waste by producing exactly what they need, when they need it. The ability to iterate rapidly through prototypes accelerates the design process, making it possible to respond to market demands with agility. Moreover,the customization capabilities foster stronger connections between brands and consumers,as customers seek products that resonate with their personal style and preferences. As we look forward, the fusion of 3D printing with emerging technologies such as AI and iot will further redefine the landscape of product design, enabling smarter, more connected experiences.
Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing Creativity in the Design Process

In the realm of industrial design, the intersection of artificial intelligence and creativity is becoming increasingly prominent. Designers are leveraging AI tools to generate unique concepts, push the boundaries of innovation, and streamline workflows. By utilizing algorithms that can analyze vast amounts of data, designers can identify emerging trends and make informed decisions, ultimately enhancing creativity in their processes. This synergy allows for a seamless blend of human intuition with machine intelligence, resulting in designs that are not only aesthetically appealing but also functionally efficient.
AI-driven software offers a variety of capabilities that empower designers to experiment and iterate more effectively than ever before. Key features include:
- Generative Design: Automating variations and solutions based on specified criteria.
- Predictive Analytics: Understanding consumer preferences and market trends through data analysis.
- Virtual prototyping: Reducing time and costs by creating 3D models for testing in a digital space.
As this technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate a profound impact on how products are conceptualized, designed, and brought to market, paving the way for a more dynamic and innovative future.
Virtual Reality: Redefining Prototyping and Consumer Engagement

In the realm of industrial design, virtual reality is revolutionizing the way prototypes are developed and refined. Designers can now immerse themselves in a fully interactive digital environment where they can manipulate 3D models as if they were tangible objects. This technology allows for immediate feedback and adjustments, enhancing collaboration among team members.Benefits of utilizing virtual reality in prototyping include:
- Real-time Iterations: Changes can be implemented on-the-fly, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced Visualization: Stakeholders can experience products in a realistic setting before physical production.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces the need for multiple physical prototypes, considerably lowering material waste.
Consumer engagement is also being transformed through immersive experiences that VR technology provides. Brands are leveraging virtual environments not only to showcase their products but to create narratives that resonate with their audiences. By inviting consumers to participate in virtual showrooms or interactive demonstrations,companies are fostering a deeper emotional connection with their products. Key advantages of this approach include:
- Personalization: Customized experiences based on user preferences enhance satisfaction.
- Increased retention: Engaging content leads to better memory recall of brand and offerings.
- Broader Reach: Virtual experiences can attract global audiences without geographical constraints.
Color Psychology: Shaping Consumer Response Through Design Choices

Color plays a pivotal role in industrial design,influencing not only the visual appeal of products but also the emotional connection consumers establish with them. By understanding the psychological impact of different colors, designers can create experiences that resonate deeply with target audiences. As an example, warm colors like red and orange may evoke feelings of energy and excitement, ideal for brands aiming to attract attention. In contrast, cool colors such as blue and green often convey calmness and trust, making them a staple choice for products in the wellness and technology sectors.
As companies increasingly seek to differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace, leveraging color psychology can enhance brand recognition and foster loyalty. Designers are now utilizing color combinations that not only comply with aesthetic principles but also align with consumer values. Some emerging trends in this space include:
- Monochromatic Schemes: Using varying shades of a single color to create depth and interest.
- bold Contrasts: Pairing vibrant colors to stimulate attention and drive engagement.
- Earth Tones: opting for colors that reflect sustainability and natural elements, aligning with eco-conscious consumer preferences.
| Color | Psychological Effect | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Excitement, passion | Food, entertainment |
| Blue | Trust, reliability | Technology, finance |
| Green | Harmony, growth | Health, eco-friendly products |
| Yellow | Optimism, clarity | Consumer goods, children’s products |
Augmented reality: Integrating and Enhancing User Interaction with Products

Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing the way consumers engage with products, transforming traditional shopping experiences into interactive adventures. as users can now simulate the presence of items in their own environment, brands are harnessing this technology to create immersive experiences that amplify product appeal. As an example, furniture companies allow customers to visualize how a couch will look in their living room before making a purchase, blending the digital and physical worlds seamlessly. This shift not only enhances user interaction but also empowers buyers, fostering a deeper connection with the products they are considering.
Moreover, AR facilitates personalization and customization, meeting the evolving expectations of today’s consumers. Brands are leveraging this technology to provide tailored experiences that resonate with individual preferences. Features such as virtual try-ons for clothing and accessories have become increasingly popular, ensuring that consumers make informed decisions without the need for physical trials. The integration of AR tools in marketing strategies can lead to higher conversion rates and increased customer satisfaction,as shoppers feel more confident in their choices. As this trend continues to grow, companies that embrace AR will not only capture attention but also redefine the consumer journey.
Transitional Spaces: Designing Environments for Versatile Uses

In an era where flexibility is paramount, transitional spaces have emerged as essential components in modern design frameworks. These environments are ingeniously crafted to adapt to diverse activities, fostering collaboration and creativity while blurring the lines between work and play. By integrating modular furniture, movable partitions, and multifunctional zones, designers create fluid areas that cater to the evolving needs of users. This adaptability not only maximizes spatial efficiency but also enhances the overall user experience, allowing individuals to seamlessly transition from one mode of interaction to another.
The future of transitional spaces involves innovative materials and smart technology that respond to real-time demands. Incorporating elements such as smart lighting, adaptive acoustics, and biophilic design enhances the ambiance and functionality, promoting well-being in versatile environments. Forward-thinking designers are embracing the idea of community-centric spaces, where the design encourages social interaction and fosters a sense of belonging. To visualize this evolution, consider the following table that highlights key features in the design of transitional spaces:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Modular Furniture | Adaptable to various activities |
| Movable Partitions | Flexible layouts to suit occasions |
| Smart Technology | Automated adjustments for comfort |
| Biophilic Elements | Enhances wellness and productivity |
Adaptive Reuse Design: Breathing new Life Into Old Structures and Products

In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, the practice of transforming old structures and products into new, functional spaces is becoming more prevalent. adaptive reuse design not only preserves the past essence of a site but also minimizes waste by repurposing materials and resources. This approach not only demonstrates respect for the past but also meets modern needs, turning forgotten buildings into vibrant community hubs. Designers are embracing a variety of elements, including:
- innovative renovations that respect the original architecture while introducing modern amenities.
- eco-friendly materials sourced from the existing structure to reduce the carbon footprint.
- Flexible layouts that encourage multifunctional usage of spaces.
- Integration of technology to enhance the user experience in adapted environments.
This trend extends beyond buildings, influencing product design as well. Designers are reimagining obsolete items,giving them new purposes and addressing contemporary needs. As a notable example, furniture made from reclaimed wood or industrial machinery finding life as art installations are just a few examples. This practice not only aligns with environmental consciousness but also promotes creativity and innovation. A closer look at the characteristics of products undergoing adaptive reuse reveals:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Functionality | Enhanced usability through inventive redesign. |
| Storytelling | Each piece carries history, telling its own narrative. |
| Aesthetics | Unique designs that stand out in contemporary spaces. |
| Resource efficiency | Minimal use of new resources, maximizing existing ones. |
Collaboration in Design: Merging Disciplines for Greater Impact on Innovation

In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, the integration of various disciplines within the design realm has become a catalyst for groundbreaking innovation. By bringing together the unique perspectives and skill sets of professionals from different backgrounds, industries can unlock a wealth of creativity and functionality. Collaboration among industrial designers, engineers, marketers, and users leads to solutions that are not only aesthetically pleasing but highly effective and user-centric. this amalgamation ensures that products are not merely developed in isolation but instead reflect a holistic understanding of the market and consumer needs.
The fusion of technology and design exemplifies this trend, as teams are increasingly leveraging tools such as 3D printing, augmented reality, and sustainable materials to rethink traditional practices. This intersection invites new approaches to problem-solving, enabling the creation of smarter, more efficient products that resonate with consumers. As the following table illustrates,effective collaboration in design can significantly enhance innovation outcomes:
| Discipline | Role in Design | Impact on Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Design | Crafting user-friendly products | Enhances usability and appeal |
| Engineering | Ensuring functionality and feasibility | Increases product reliability |
| Marketing | Understanding consumer behavior | aligns products with market desires |
| Sustainability Experts | Incorporating eco-friendly practices | Minimizes environmental impact |
Impact of Globalization on Local Industrial Design Trends and Aesthetics

As boundaries blur in an increasingly interconnected world, the fusion of global influences dramatically reshapes local industrial design landscapes. Designers are drawing inspiration from a plethora of international sources,leading to eclectic aesthetics that combine cultural symbols with modern functionality.This cross-pollination creates a rich tapestry of design possibilities, where elements such as sustainability, technology, and minimalist forms converge to form stunning, innovative products that resonate with diverse audiences. Cultural authenticity becomes a pivotal theme, as local artisans infuse traditional techniques with contemporary styles, providing a fresh narrative that elevates their work on a global stage.
Simultaneously, the influx of global design trends empowers local industries to experiment with new materials and technologies.Local designers are increasingly adopting approaches that prioritize user experience and sustainability while maintaining their unique identity. As an example, the shift towards eco-friendly materials not only addresses environmental concerns but also encourages the revival of regional craftsmanship. The local market now sees a blend of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technologies such as 3D printing, making it possible to create intricately designed products that appeal to modern sensibilities. With this dynamic interplay, the landscape of industrial design continues to evolve, suggesting that the future will likely be marked by a harmonious combination of global influences and local narratives.
| Trend | Description | Local Impact |
|---|---|---|
| eco-Friendly Materials | Use of sustainable materials to reduce environmental impact. | Revival of traditional techniques, fostering local craftsmanship. |
| Minimalism | Simple, clean designs that emphasize functionality. | Encourages local designers to streamline offerings without losing identity. |
| Smart Technology Integration | Incorporating IoT and smart features into products. | increases global competitiveness for local products. |
Future Outlook
As we stand at the crossroads of creativity and technology, the landscape of industrial design continues to evolve at a breathtaking pace. The trends explored in this article are not just fleeting fads; they represent a fundamental shift in how we envision the objects, environments, and experiences that will define our future.From sustainable practices that honor our planet to the integration of smart technologies that enhance connectivity, the choices we make today will undoubtedly shape the innovations of tomorrow.As designers, engineers, and visionaries come together to push boundaries, they invite us all to participate in a dialog about the values and aspirations that will guide us forward. in embracing these trends, we open the door to a world brimming with potential, where functionality meets aesthetic and the human experience is at the heart of every design.
The future is not something we enter; it is indeed something we create.So, let us take inspiration from these emerging trends and embark on this exciting journey of exploration together. The innovations that await us are limited only by our creativity. As we move forward,let us be thoughtful stewards of design,crafting solutions that not only meet the needs of today but also honor the dreams of generations to come.
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.




